Inheritance is a relationship between objects which allows the transfer and reuse of information. It is common when defining classes, for different classes to share traits, such as similar methods and variables. This is especially useful in creating objects to be used in databases.
In inheritance, a main concept is the relationship between superclasses and subclasses. The superclass is a class which passes traits, variables and methods, to subclasses. Subclasses use these traits for their unique purposes while avoiding repetition in code.
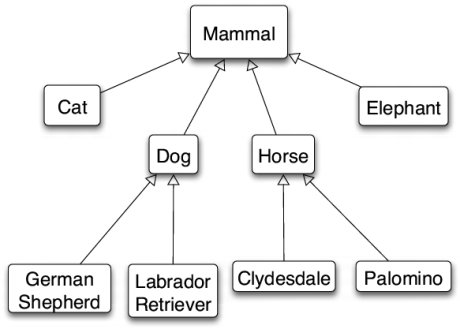
Source: https://www.developerdotstar.com/mag/articles/pugh_interface_oriented.html
In the above example, the superclass Mammal has a relationship with the subclasses: Cat, Dog, Horse, and Elephant. These subclasses inherit information relative to being a mammal from the Mammal class. The kind of information is relative to the use of the classes. Similarly, the Dog class is the superclass for GermanShepard and LabradorRetriever would pass information relative to dogs in this situation.
Although Dog is the subclass of Mammal, it is still the superclass for GermanShepard and LabradorRetriever. The relationship of superclass and subclass is all relative.
Although, there is an implied relationship between the subclass and its superclass’s superclass. The superclass of a superclass is not a “supersuperclass”.. This is not true because inheritance relationships only span one layer of the hierarchy.
Here is the syntax for creating a subclass:
public class A {
...
}
public class B extends A { // Class B is a subclass of class A
...
}
In order to define class B as a subclass of A, in the class signature line, the extends keyword is required, followed by referring to the superclass. This will cause class B to inherit all public and protected methods and fields in class A.
Here is an example of the above inheritance hierarchy:
public class Mammal {
private int age;
private int weight;
private int height;
private int name;
public Mammal(int a, int w, int h, int n) {
age = a;
weight = w;
height = h;
name = n;
}
public int getWeight() {
return weight;
}
public int getHeight() {
return height;
}
}
public class Dog extends Mammal {
private String breed;
public Dog(int a, int w, int h, int n, String b) {
super(a, w, h, n);
breed = b;
}
public String getBreed() {
return breed;
}
public void bark() {
System.out.println("Bark! Bark! Bark!");
}
}
public class GermanShepard extends Dog {...}
public class LabradorRetriever extends Dog {...}
The subclass, must always have a constructor which calls the constructor in the superclass using super(), this call to the super must be the first line in the constructor.
Lesson Quiz
1. Which keyword is used to create a subclass??
2. True or false, a superclass has more information than its subclass?
Written by James Richardson
Notice any mistakes? Please email us at learn@teamscode.com so that we can fix any inaccuracies.